An injured cetacean, caused by a vessel.
Source: https://sanctuaries.noaa.gov/science/sentinel-site-program/hawaiihumpbackwhale/vessel-impacts.html
An injured cetacean, caused by a vessel.
Source: https://sanctuaries.noaa.gov/science/sentinel-site-program/hawaiihumpbackwhale/vessel-impacts.html
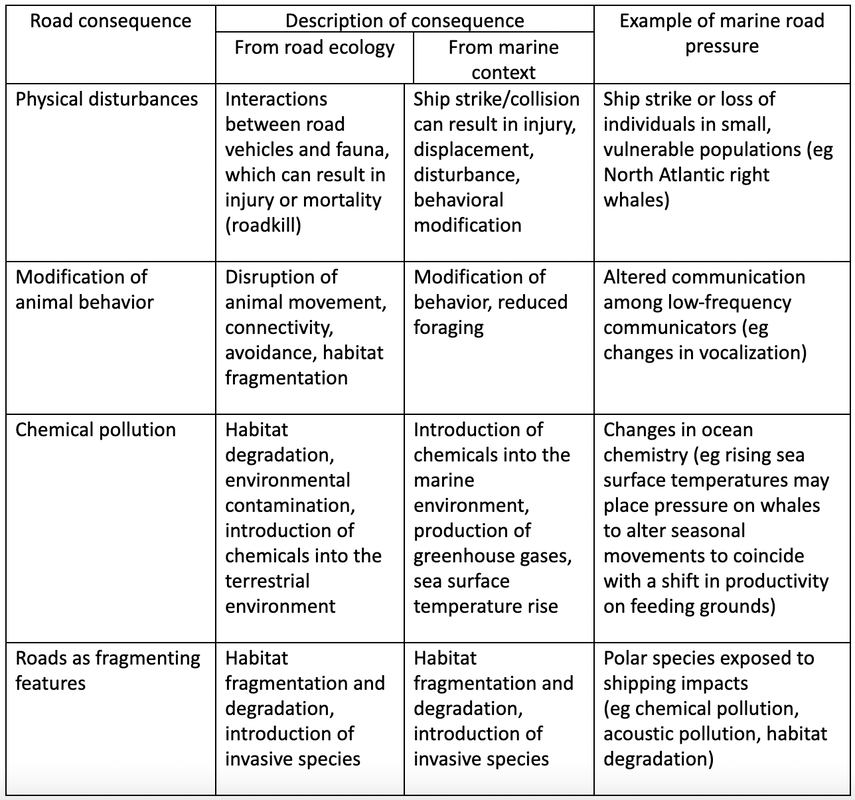
Physical disturbances
Physical disturbances are direct interactions between vehicles and animals along roadways.
- Marine giants such as whales are vulnerable to shipping impacts due to biological traits like the need to frequent the surface often to breathe.
- Ship strike is a result of unintentional interactions and can be fatal or result in serious trauma or injury
- For some populations, such as the North Atlantic right whale (Eubalaena glacialis), ship strikes have been responsible for over half of all mortalities in recent decades
Modification of animal behaviour
Modification of behaviour refers to an animal's response to road presence or vehicle activity. Unlike terrestrial roads, marine roads are not permanent structures, but underwater shipping noise and the presence of ships in the marine environment may act as a persistent reminder of marine road presence.
- Shipping produces low-frequency sounds are the largest contributor of anthropogenic noise in the ocean.
- These low-frequency sounds range from 5 to 500 hertz (Hz), and global shipping networks have added an estimated 12 decibels (dB) to ocean ambient noise levels.
- Exposure of marine giants to shipping noise may induce a number of behavioural modifications, including avoidance, altered foraging and movement patterns, habituation, and disrupted communication.
- Whales modify the way they communicate
- Such variability in response behaviours complicates understanding the consequences of marine road presence and shipping noise across species.
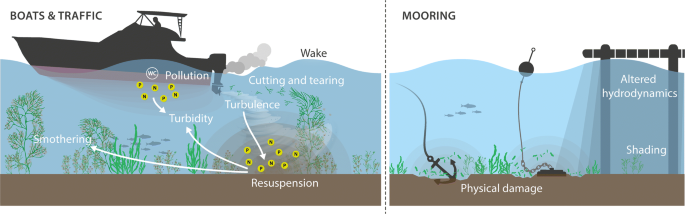
Chemical Pollution
Pollution derived from marine roads refers to the direct and indirect contribution of waste produced by shipping into the oceans.
- Dispersion of chemicals resulting from the spillage of oil into the ocean.
- Severe oil spills in the marine environment can cause serious harm; for example, a large proportion of killer whales.
- Shipping now produces close to 1 billion metric tons of CO2 annually with emissions projected to increase by 50–250% by 2050.
- Shipping emissions contribute to already occurring changes in marine conditions, such as increasing sea surface temperatures (SSTs) and ocean acidification.
- Changes in SST may alter the distribution and abundance of prey species, which in turn influence the foraging behaviours and diets of marine giants.
Roads as fragmenting features
New marine roads are being developed as a direct result of climate change opening up previously non-navigable waters, such as the recent emergence of ice-free lanes across the Arctic.
- New marine roads like the Northwest Passage and the Northeast Passage have shortened shipping routes between Europe and Asia by 35–60%, an economically preferable alternative to routes via the Suez and Panama canals.
- Potential environmental benefits would include fewer emissions, reduced fuel requirements, and less time spent travelling between locations.
- Although these new shipping routes provide immense economic benefits to the shipping industry, there are numerous potentially adverse environmental consequences to their use.
- Marine pollution is likely to increase in Arctic regions, as will the risk of bio-invasions due to the spread of invasive species released via ballast water.
- As marine roads in the Arctic become used more and more frequently for resource extraction, tourism, and cargo transport, concomitant shipping-related impacts on marine giants are also likely to intensify.
- New marine roads threaten a number of endemic, ice-associated whale species, including narwhals, beluga whales, and bowhead whales.
Physical disturbances are direct interactions between vehicles and animals along roadways.
- Marine giants such as whales are vulnerable to shipping impacts due to biological traits like the need to frequent the surface often to breathe.
- Ship strike is a result of unintentional interactions and can be fatal or result in serious trauma or injury
- For some populations, such as the North Atlantic right whale (Eubalaena glacialis), ship strikes have been responsible for over half of all mortalities in recent decades
Modification of animal behaviour
Modification of behaviour refers to an animal's response to road presence or vehicle activity. Unlike terrestrial roads, marine roads are not permanent structures, but underwater shipping noise and the presence of ships in the marine environment may act as a persistent reminder of marine road presence.
- Shipping produces low-frequency sounds are the largest contributor of anthropogenic noise in the ocean.
- These low-frequency sounds range from 5 to 500 hertz (Hz), and global shipping networks have added an estimated 12 decibels (dB) to ocean ambient noise levels.
- Exposure of marine giants to shipping noise may induce a number of behavioural modifications, including avoidance, altered foraging and movement patterns, habituation, and disrupted communication.
- Whales modify the way they communicate
- Such variability in response behaviours complicates understanding the consequences of marine road presence and shipping noise across species.
Chemical Pollution
Pollution derived from marine roads refers to the direct and indirect contribution of waste produced by shipping into the oceans.
- Dispersion of chemicals resulting from the spillage of oil into the ocean.
- Severe oil spills in the marine environment can cause serious harm; for example, a large proportion of killer whales.
- Shipping now produces close to 1 billion metric tons of CO2 annually with emissions projected to increase by 50–250% by 2050.
- Shipping emissions contribute to already occurring changes in marine conditions, such as increasing sea surface temperatures (SSTs) and ocean acidification.
- Changes in SST may alter the distribution and abundance of prey species, which in turn influence the foraging behaviours and diets of marine giants.
Roads as fragmenting features
New marine roads are being developed as a direct result of climate change opening up previously non-navigable waters, such as the recent emergence of ice-free lanes across the Arctic.
- New marine roads like the Northwest Passage and the Northeast Passage have shortened shipping routes between Europe and Asia by 35–60%, an economically preferable alternative to routes via the Suez and Panama canals.
- Potential environmental benefits would include fewer emissions, reduced fuel requirements, and less time spent travelling between locations.
- Although these new shipping routes provide immense economic benefits to the shipping industry, there are numerous potentially adverse environmental consequences to their use.
- Marine pollution is likely to increase in Arctic regions, as will the risk of bio-invasions due to the spread of invasive species released via ballast water.
- As marine roads in the Arctic become used more and more frequently for resource extraction, tourism, and cargo transport, concomitant shipping-related impacts on marine giants are also likely to intensify.
- New marine roads threaten a number of endemic, ice-associated whale species, including narwhals, beluga whales, and bowhead whales.
Useful links:
-https://esajournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/fee.1987
-https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmars.2020.00637/full
-https://www.marineinsight.com/environment/effects-of-noise-pollution-from-ships-on-marine-life/
-https://eponline.com/Articles/2017/03/27/The-Environmental-Impacts-of-Boating.aspx
-https://ec.europa.eu/environment/integration/research/newsalert/pdf/87na2_en.pdf
-https://wildwhales.org/threats/vessel-disturbance/
-https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Environmental_effects_of_shipping
-https://www.dynamo.vc/blog-posts/the-environmental-impact-of-maritime-freight
-https://mol.disclosure.site/en/themes/103
Videos:
-https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fRkTIv8_pdA
-https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=RDx8i68nebY
-https://esajournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/fee.1987
-https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmars.2020.00637/full
-https://www.marineinsight.com/environment/effects-of-noise-pollution-from-ships-on-marine-life/
-https://eponline.com/Articles/2017/03/27/The-Environmental-Impacts-of-Boating.aspx
-https://ec.europa.eu/environment/integration/research/newsalert/pdf/87na2_en.pdf
-https://wildwhales.org/threats/vessel-disturbance/
-https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Environmental_effects_of_shipping
-https://www.dynamo.vc/blog-posts/the-environmental-impact-of-maritime-freight
-https://mol.disclosure.site/en/themes/103
Videos:
-https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fRkTIv8_pdA
-https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=RDx8i68nebY